
The bridge consists of two or more crowns, depending on how many teeth there are, and one false or more teeth in between. False teeth are called bridges and are made of metal alloys - base metal or noble metal alloy -, porcelain or a combination of the above. Bridges rely on either our natural teeth or implants.
When do we need dental bridges
- A missing tooth, especially one of the front teeth, affects our appearance in a negative way.
- The loss of a tooth changes the distribution of pressure exerted during chewing by burdening the remaining teeth.
- The loss of many teeth can seriously affect a person's ability to chew, forcing them to modify their diet and reduce the quality of their diet..
Conditions for installing a dental bridge
- The number of consecutive missing teeth should not be large. A bridge should not replace more than three consecutive missing teeth. Of course if there are two empty spaces but mediated by natural teeth, the total number of teeth that can replace a bridge is greater.
- There should be teeth on either side of the empty space, so that the bridge has support at both ends. If this condition does not apply, there are two possible solutions. The best and safest is to place an implant that will play the role of the tooth-support. The second but more precarious is the use of a bridge with a cantilever, ie supported only at one end.
- The natural teeth on which the bridge will rest must be healthy. If there is caries, the tooth will be cleaned during the preparation process. If there is a lot of damage it may be necessary to denervate and use an endotracheal shaft to better support the bridge.
- The natural teeth on which the bridge will rest must be stable. A tooth with mobility cannot be used as a base for a bridge. The dentist will examine the mobility of the tooth and the degree of its support in the jaw bone before deciding if it should be kept or extracted.
- There should be no symptoms of periodontal disease. Gingivitis or periodontitis must have been treated and the gums fully restored before a dental bridge can be taken.
- There should be no signs of neglect of oral hygiene. If the patient is known to systematically ignore oral hygiene, the life expectancy of a dental bridge is significantly reduced.
Types of dental bridges
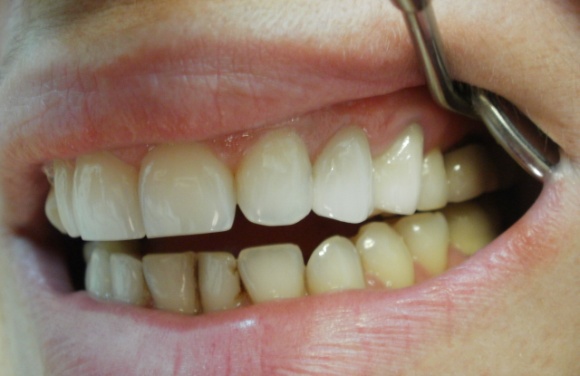
- Classical dental bridges.The classical dental bridges consist of one or more artificial teeth attached to two crowns that are placed on the teeth on either side of the missing ones. The two hoops at the ends of the bridge stabilize it in place. It is the most common method of building a dental bridge.
- Dental bridges Maryland. This type of bridge got its name from the University of Maryland where the relevant technique evolved. The difference is that the artificial teeth rest on a metal frame that extends to the inner lingual side. The support at its ends is not made with hoops as in the classic bridges, but with 2 metal fins that protrude and which are glued to the back of the adjacent teeth-brackets. The advantage is that much less amount of dental tissue is removed from the healthy teeth used to support the bridge, while they are also more economical in terms of price. The disadvantages of the Maryland bridge type are that it can be detached more easily than conventional bridges and is therefore only used when one or two, and especially the front, teeth are missing.
- Tooth bridges with cantilever. This type of bridge is used when no tooth is available to support the bridge on one side of the missing teeth. In these cases, a bridge is constructed supported by a rim on one side only, having as a cantilever (hanging) the tooth that it replaces. In general, cantilever bridges are emergency solutions, eg when a rear molar is missing, or low-cost solutions to save the cost of an extra rim. However, cantilever bridges are low strength and should be avoided if possible.
- Dental bridges supported by implants. When many consecutive teeth are missing, when there are no natural teeth on one side of the empty space, or when the existing teeth are weak enough to withstand the increased pressure, it is very difficult to place a bridge safely. The solution to this problem is the placement of one or more dental implants which play the role of the supporting teeth.
- Metal ceramic bridges. Metal-ceramic bridges are the ones that are widely used today. The cases that make them up consist of a metal frame which is completely covered with ceramic material (porcelain). They offer great durability and can be used in any case where a bridge needs to be installed. They are cheaper than all-ceramic bridges but more expensive than metal-acrylic ones.A disadvantage of metal-ceramic bridges is the presence of a dark metal frame, which although completely covered with porcelain does not allow light to penetrate the crown as is done in natural teeth, giving a relative opacity to the final restoration. Also at the borders of the crowns near the gums appears a dark unsightly line that 'betrays' the border of the bridge.
- All-ceramic bridges. All-ceramic bridges are a new type, free of metal core. They have a porcelain frame which is covered by a special type of ceramic material. The absence of a metal frame gives a significant advantage in aesthetics and naturalness compared to other types of bridges, because only porcelain can mimic the transparency of the enamel of the natural tooth..The disadvantage of all-ceramics is their higher cost and relatively reduced durability, compared to metal-ceramics. For this reason their use is limited to the anterior region of the mouth and in cases of missing a tooth only.
- Zirconium Bridges Their frame consists of zirconium oxide coated with porcelain. Zirconia is white in color and allows light to pass through the porcelain while being very resistant to pressure. A zirconium bridge combines the aesthetic advantages of an all-ceramic bridge with increased durability, but it is also the most expensive option in terms of price (almost twice the cost of a metal-ceramic bridge).
- Metal-acrylic bridges. Metal-acrylic bridges are metal on the inside and have a plastic coating on the outside visible side. It is an economical choice but not recommended due to their low durability and rapid aesthetic deterioration.
- Metal bridges. Metal bridges are made entirely of metal, usually gold. They are rarely used now despite their great durability and lower cost as they are not aesthetically acceptable.
Procedure for construction and installation of a dental bridge
Bridges are structures that are permanently attached to the mouth, on existing teeth that are properly shaped, replacing the missing teeth. The process of building and installing a dental bridge requires at least 3 visits to the dentist.- All the problems that the natural teeth on which the bridge will be supported are restored. This may involve caries removal and sealing or may require endodontic treatment (denervation) and cast shaft placement. Periodic problems should be addressed before the bridge preparation process begins. Also if there are no natural teeth to support it but implants will be needed, they should have been placed in time to be fully integrated.
- Local anesthesia is given and the abutment teeth are chewed and chewed sideways to create the necessary space for the crown material that will support the bridge. It is usually required to remove about 1 to 1.5 millimeters of dental tissue.
- After the grinding of the teeth is completed, a soft imprint material is placed on the teeth and an imprint ('measures') is obtained, based on which the dental technician will build the bridge.
- We protect the prepared teeth with temporary crowns.
- Finally, the patient and the dentist decide on the material from which the bridge will be made.
- After the temporary crowns are removed, the bridge frame is tested to see if it fits properly on the tooth and gums.
- The appropriate color for the bridge is selected to match the color of the natural teeth. If the patient desires to have teeth whitening this must be done BEFORE the choice of color.
- We replace the temporary crowns.
- The bridge, after being prepared by the dental laboratory, is placed in the mouth and, if its application is correct, it is permanently cemented to the abutment teeth.
How to take care of the dental bridges
It is important that the teeth-supports as well as the bone that supports them remain in good condition. This is achieved with good oral hygiene:
Brushing your teeth, ideally, after every meal, and interdental cleaning - dental floss and interdental brushes. This will prevent tooth loss by preventing tooth decay and periodontal disease. With frequent re-examinations at the dentist, possible problems are checked at an early stage, when the treatment will have a better prognosis. Finally, it is important to maintain a careful and healthy diet.
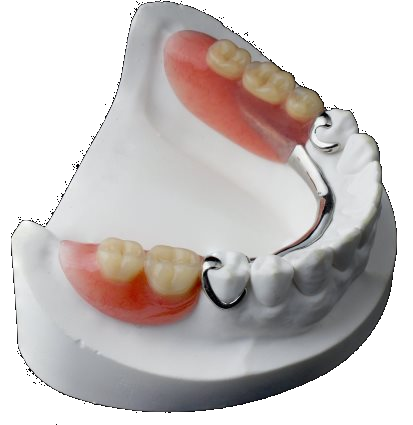
They usually contain a metal grid, on which the partial denture rests. They are combined with hooks - metal or acrylic - that hug the teeth or with precision connectors. Usually, crowns are made on the tooth braces, together with precision joints, because this way the retention of the partial denture in the mouth is better achieved. Joints increase the cost of dentures, but give a better aesthetic result, compared to hooks.
The construction of a partial denture requires several appointments. High-precision prints for mold making are essential for proper workmanship.
At first, you may feel uncomfortable with the denture in your mouth. That makes perfect sense. It is normal to have severe salivation or some discomfort when talking and chewing. Gradually, the discomfort will subside as the muscles and tissues of the mouth adjust..
Placing and removing dentures requires a little practice. Under no circumstances should you use too much force to install it as it may break the hooks or links. Initially, you may need to wear your dentures constantly. This may be awkward at first, but it is the fastest way to identify areas that may need repair. If the denture pushes too hard on an area of the mouth, this spot will be irritating. It is necessary to make corrections in the denture in order to relieve the specific point.
Start with soft foods cut into small pieces. Chew on both sides of the mouth to balance the chewing pressures. Avoid foods that are particularly sticky or hard. A few dentures will also improve speech. If you find it difficult to pronounce some words, you should practice saying them out loud. Gradually, you will get used to them and pronounce them normally.
The cleaning of the partial denture is necessary and must be done with CAUTION, with the same frequency that we brush our natural teeth. You can clean the partial denture with a SOFT toothbrush and some cleaner, just as you would brush your teeth. This will protect your dentures from permanent pigmentation. When cleaning it, be careful not to drop it on the floor.
The denture must remain in a moist environment so as not to lose its shape. At night, if you take it out of the mouth, it should be kept in a container with water.
Over time, your dentures will need to be checked for proper retention. As we grow older, some physiological changes occur in our mouth. The bone and gums recede, losing its proper fit. In this case, the denture should be repaired to avoid serious problems, such as infections, sores and damage to the teeth.













 Services
Services